Image
Objective
Learn popliteal sciatic nerve block procedure: Injection of local anaesthetic around the Sciatic Nerve while utilising Ultrasound Guidance to maintain visualisation of the block needle.
Procedure Description:
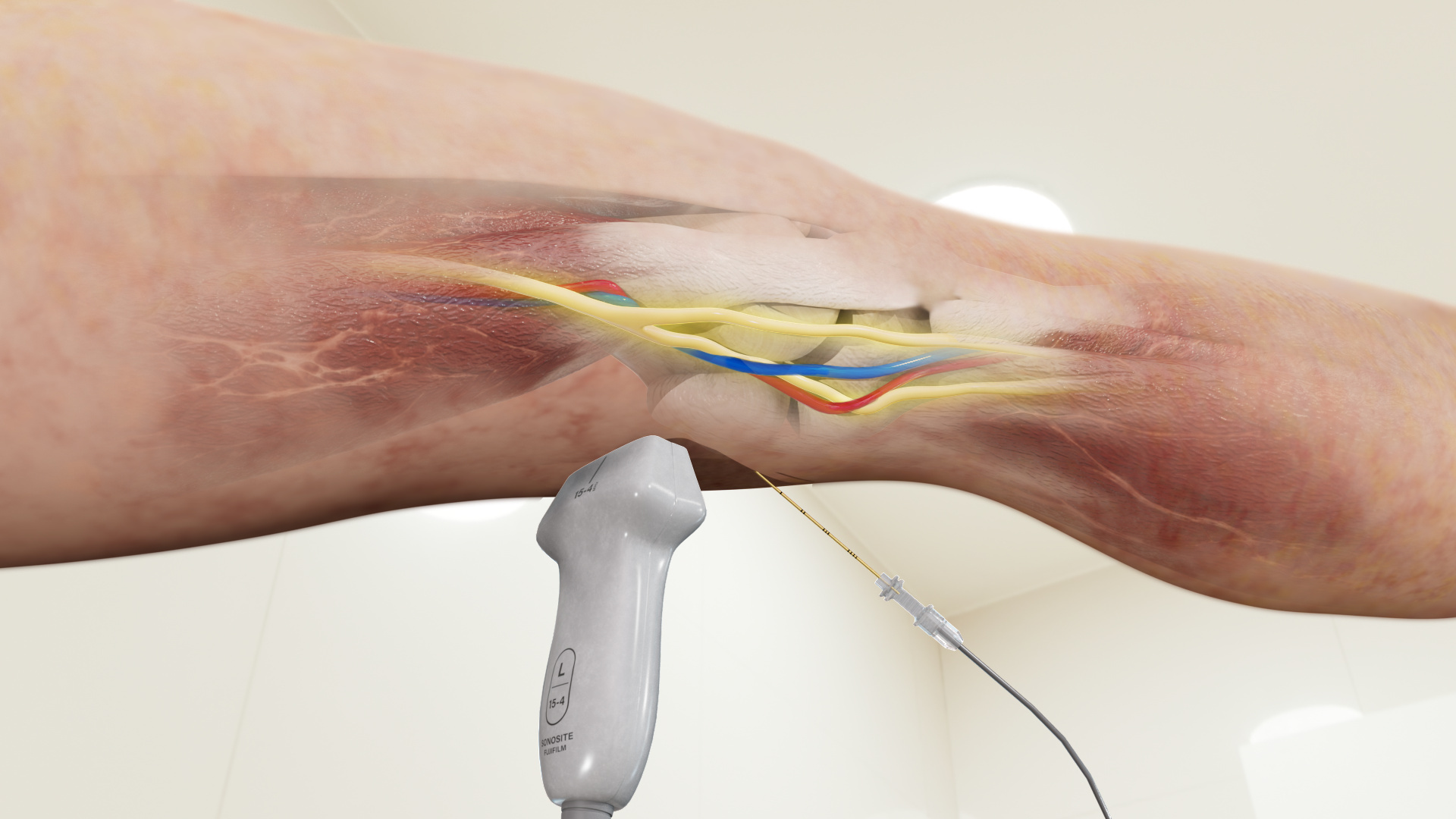
- Begin by elevating the operative leg onto a table or a leg holder with the patient in the supine position.
- The ultrasound transducer is placed at the Popliteal crease in the transverse orientation.
- The Popliteal Artery is identified within the Popliteal Fossa and the Tibial Nerve is identified superficial and lateral to the Popliteal Artery with the Peroneal Nerve identified superficial and lateral to the Tibial Nerve.
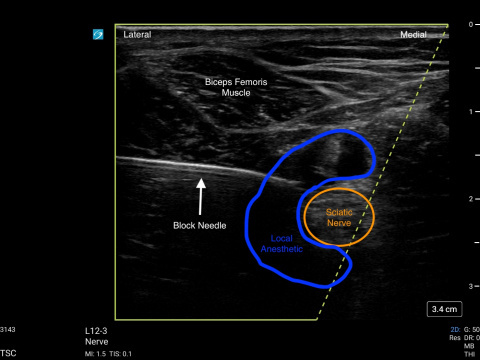
- Move the transducer proximal following the Tibial and Peroneal Nerves until they merge to form the Sciatic Nerve. The injection is performed at this level.
- The block needle is inserted using the in-plane approach from lateral to medial.
- Local anaesthetic is deposited around the Sciatic Nerve.
- Commonly performed for surgery of the knee, lower leg, foot, and ankle.
Image
Clinical Pearls
Patient Positioning:
Supine leg elevated
Transducer:
Teaching Points:
- The block needle may be repositioned under ultrasound guidance to ensure adequate spread of local anaesthetic around the Sciatic Nerve.
- A nerve stimulator may be used to ensure the injection is in close proximity to the Sciatic Nerve.
- The Sciatic Nerve Block may also be performed in the prone position.
- The Sciatic Nerve Block provides both a motor and sensory block.
- The Sciatic Nerve Block will inhibit early postoperative ambulation.
- A low volume of local anaesthetic (5-10ml) will provide a Sciatic Block that lasts 20-24 hours.
- See the related video Ultrasound-Guided Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block.
Click to download the guide today.

